Molecular Microbiology (Virology)
Institute of Medical Microbiology and Hygiene
University Regensburg
Funding: The Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) Title: HIV Vaccine Targeting via DNA Origami Nanoparticles to lymph nodes to promote Germinal Center formation
HIV has so far defied all attempts to develop an effective vaccine against it. Nine efficacy trials testing several vaccine candidates have been conducted in the last 25 years, with only one of them resulting in very modest, insufficient protection. One trial, PrEPVacc, is still ongoing.

Funding: Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
Neutralizing antibodies provide suitable protection against either infection with SARS-CoV-2 virus or at least protection against severe illness e.g. corona virus induced disease 19 (COVID19) and death. To achieve the desired project aims, different competences are required. Therefore, the project brings together experts from the fields of analytical chemistry, molecular immunology, and virology collaboration with biotech industry to generate a product ready to enter the market. Moreover, this platform can be used in the future to provide a chassis for test assays to detected potent immunity against new emerging virus that might come.Funding: European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme
The European HIV Vaccine Alliance (EHVA) – funded by the European Union’s H2020 Program – aims at discovering and evaluating new prophylactic and therapeutic HIV-1 vaccine candidates. The program is coordinated by Prof. Yves Lévy (INSERM, Paris) and Prof. Giuseppe Pantaleo (CHUV, Lausanne) and comprises 39 partners from 15 countries. Within the alliance, the University of Regensburg coordinates the Vaccine-Discovery- Workpackage for novel antigen candidates, delivery systems and formulations.
Funding: Innovate UK Title: Clinical trial of a DIOS Trivalent Haemorrhagic Fever Vaccine
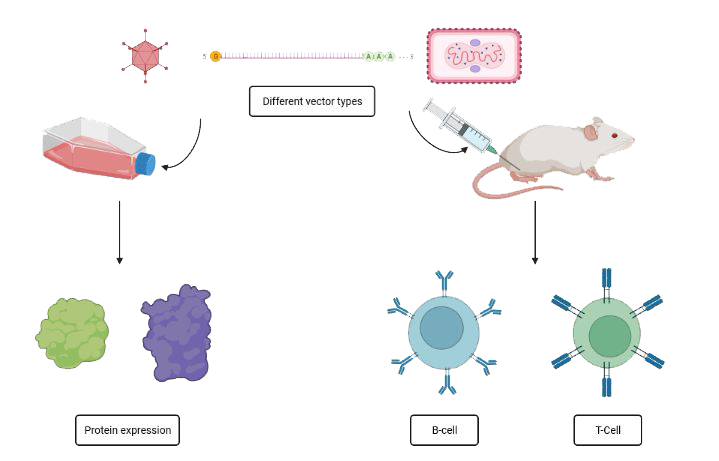
The HFVac3-project is based on the predecessor projects EVAC and Tri-LEMvac that also were funded by Innovate UK. Within the EVAC project, a streamlined process for vaccine generation starting with in silico design of antigen sequences, over the generation of delivery vectors (DNA, adenovirus, vaccinia virus) and rapid testing for immunogenicity in small animal models (mice and guinea pigs) – all steps to be completed within one year – had been developed.
Funding: EU – Horizon 2020
Full title: European Consortium for the Development of Novel Therapies against Viruses such as SARS-CoV-2, HIV, Influenza or Hepatitis
Current antiviral drugs constitute small molecules that target and inactivate typical proteins or enzymes of selected viruses. Within the EU-funded Virofight project (coordinated by the Technical University of Munich), nanometer sized shells shall be developed that enclose viruses, thus neutralizing them. This new approach might allow targeting of diverse viruses by employing the same method.
The aim is to develop prototypes of nano-shells and to principally prove that they are capable of enclosing different viruses. Different technologies will be applied during the development of these biocompatible nano-shells such as DNA origami, protein design and in-vitro-evolution. The interior of the shells will be coated with molecules that are tuned to certain viruses and ensure a strong and specific interaction. These binding effects shall be assessed for different viruses on a laboratory scale. To achieve the desired project aims, different competences are required. Therefore, the project brings together experts from the fields of supermolecular chemistry, molecular nano-engineering and virology.
Within the Virofight consortium, the Wagner Lab is involved in the evolution of those components that provide the nano-shells with specificity toward the different viruses. Moreover, the team will test the efficacy of the nano-shell protoypes against HIV, influenza or corona viruses.
Project partners:
Technical University Munich (TUM; Germany) – project coordinator
Molecular Microbiology (Virology), Institute of Medical Microbiology and Hygiene, University of Regensburg (Germany)
Aarhus University (Denmark)
ARTTIC S.A.S. (France)
National Institute of Chemistry (Slovenia)
Further information:
Virofight Website
EU Cordis portal
Our press release on VIROFIGHT project
Press release on the hybrid VIROFIGHT Symposium on “Antiviral Biologics” on Friday, 22nd November 2024 in Garching, Germany

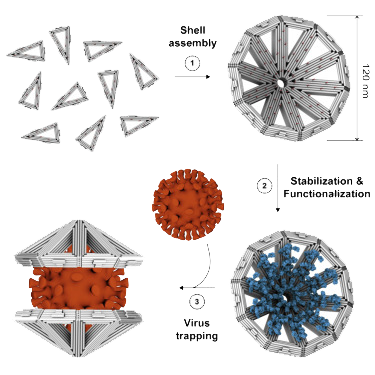
Assembly and functionalization schematic of DNA-Origami nanoshells as published in Monferrer et al, Science physical reports, 2023 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrp.2022.101237
Funding: Eurostars Full title: Treating cancer by targeting endogenous retroviral fossils within the human genome
Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) are transposable retroviral elements accounting for about 8 % of the human genome. They are ancient relicts acquired through multiple infections of the germ line by now extinct exogenous retroviruses.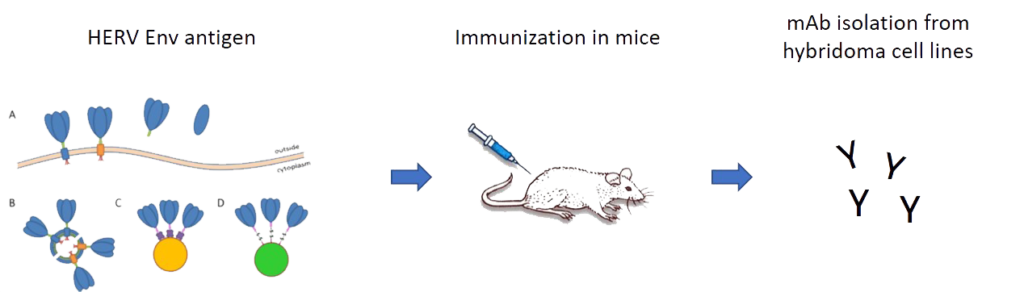

Funding: Bavarian State Ministry of Science and Arts (StMWK) and National Research Network of the University Medicine (NUM; applied surveillance and testing; B-FAST)
Full title:Tirschenreuth-Kohorte-Covid-19 study
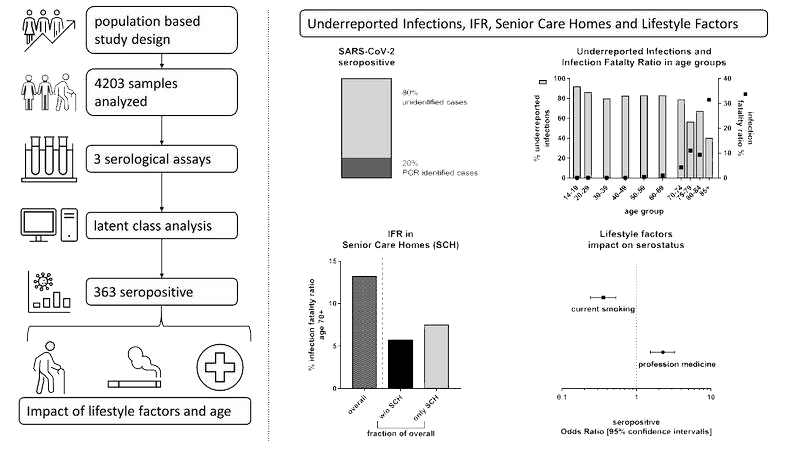
The Bavarian county of Tirschenreuth was one of the first “Corona hot-spot” areas in Germany, as it was hit by a severe outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 connected to a beer-festival in March 2020, which lead to a high incidence of (PCR-positive) cases and a remarkably high case fatality rate (CFR) of 11.5%. As it was unclear at this point of time if the CFR is based on insufficient identification of cases or on other unknown effects, the Tirschenreuth-Kohorte-Covid-19 (TiKoCo19) study was started to determine the actual seroprevalence in the county in collaboration with the FAU Erlangen and the LMU Munich.
The blood samples are analyzed for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies utilizing a variety of tests: the UR inhouse-ELISA, the commercially available Roche COBAS-Elecsys tests and further commercially available tests (e.g. by Shenzhen YHLO Biotech the market leader in Asia). On top, other tests as surrogate and wildtype neutralization assays, binding/neutralization assays regarding the arising variants of concern are used. The aim of the project is to monitor SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence, the surveillance detection ratio and infection fatality ratio as well as antibody stability, reinfections, vaccine effects and other possible effects/correlations with e.g. age, profession or lifestyle factors.
Partners:
Molecular Microbiology (Virology), Institute of Medical Microbiology and Hygiene, University of Regensburg
Institute of Clinical Microbiology and Hygiene, University Hospital Regensburg
Institute of Clinical and Molecular Virology, University Hospital Erlangen
Statistical Consulting Unit StaBLab, Department of Statistics, LMU Munich
Department of Genetic Epidemiology, University of Regensburg
Institute of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, University Hospital Regensburg
University Children’s Hospital Regensburg (KUNO) at the Hospital St. Hedwig of the Order of St. John, University of Regensburg
Bayerisches Rotes Kreuz, Kreisverband Tirschenreuth
Department of Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU)
The COVID-19 vaccines approved in Germany show a high effectiveness against laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 diseases. Although the vaccines are highly effective in the pivotal studies, it can be assumed that there will a significant number of breakthrough infections due to the large number of those who will be vaccinated in a short time and emerging new virus variants.